貨號(hào)
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN42034M-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
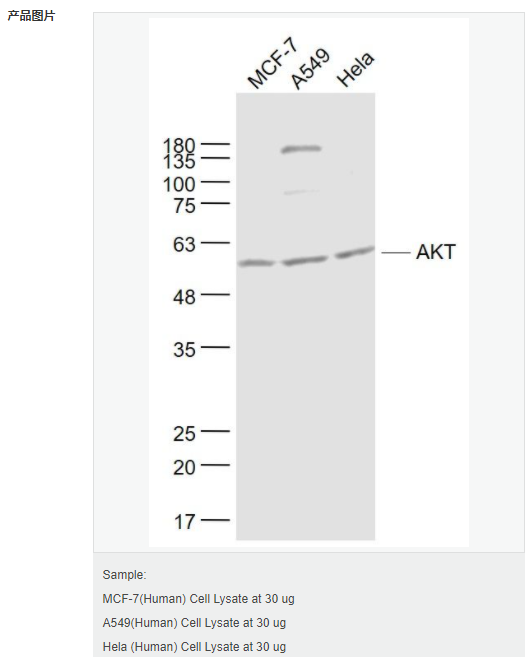
交叉反應(yīng):Human 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,ELISA
BN42034M-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | AKT |
| 中文名稱 | 蛋白激酶B單克隆抗體 |
| 別 名 | AKT 1; AKT; AKT1; AKT-1; AKT1_HUMAN; C AKT; cAKT; MGC9965; MGC99656; Oncogene AKT1; PKB; PKB alpha; PKB-ALPHA; PRKBA; Protein Kinase B Alpha; Protein kinase B; Proto-oncogene c-Akt; RAC Alpha; RAC alpha serine/threonine protein kinase; RAC; RAC PK Alpha; Rac protein kinase alpha; RAC Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase; RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; RAC-PK-alpha; v akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; vAKT Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 腫瘤 細(xì)胞生物 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) 信號(hào)轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo) 細(xì)胞凋亡 激酶和磷酸酶 |
| 抗體來(lái)源 | Mouse |
| 克隆類型 | Monoclonal |
| 克 隆 號(hào) | 3H2 |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-1000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 56kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞核 細(xì)胞漿 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human AKT:420-479/479 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein G |
| 儲(chǔ) 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011] Function: AKT1 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Phosphorylates STK4/MST1 at 'Thr-120' and 'Thr-387' leading to inhibition of its: kinase activity, nuclear translocation, autophosphorylation and ability to phosphorylate FOXO3. Phosphorylates STK3/MST2 at 'Thr-117' and 'Thr-384' leading to inhibition of its: cleavage, kinase activity, autophosphorylation at Thr-180, binding to RASSF1 and nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates SRPK2 and enhances its kinase activity towards SRSF2 and ACIN1 and promotes its nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-259' and negatively regulates its activity. Phosphorylation of BAD stimulates its pro-apoptotic activity. AKT1-specific substrates have been recently identified, including palladin (PALLD), which phosphorylation modulates cytoskeletal organization and cell motility; prohibitin (PHB), playing an important role in cell metabolism and proliferation; and CDKN1A, for which phosphorylation at 'Thr-145' induces its release from CDK2 and cytoplasmic relocalization. These recent findings indicate that the AKT1 isoform has a more specific role in cell motility and proliferation. Phosphorylates CLK2 thereby controlling cell survival to ionizing radiation. Subunit: Interacts (via the C-terminus) with CCDC88A (via its C-terminus). Interacts with GRB10; the interaction leads to GRB10 phosphorylation thus promoting YWHAE-binding. Interacts with AGAP2 (isoform 2/PIKE-A); the interaction occurs in the presence of guanine nucleotides. Interacts with AKTIP. Interacts (via PH domain) with MTCP1, TCL1A AND TCL1B. Interacts with CDKN1B; the interaction phosphorylates CDKN1B promoting 14-3-3 binding and cell-cycle progression. Interacts with MAP3K5 and TRAF6. Interacts with BAD, PPP2R5B, STK3 and STK4. Interacts (via PH domain) with SIRT1. Interacts with SRPK2 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Interacts with RAF1. Interacts with TRIM13; the interaction ubiquitinates AKT1 leading to its proteasomal degradation. Interacts with TNK2 and CLK2. Interacts (via the C-terminus) with THEM4 (via its C-terminus). Interacts with and phosphorylated by PDPK1. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cell membrane. Note=Nucleus after activation by integrin-linked protein kinase 1 (ILK1). Nuclear translocation is enhanced by interaction with TCL1A. Phosphorylation on Tyr-176 by TNK2 results in its localization to the cell membrane where it is targeted for further phosphorylations on Thr-308 and Ser-473 leading to its activation and the activated form translocates to the nucleus. Tissue Specificity: Expressed in prostate cancer and levels increase from the normal to the malignant state (at protein level). Expressed in all human cell types so far analyzed. The Tyr-176 phosphorylated form shows a significant increase in expression in breast cancers during the progressive stages i.e. normal to hyperplasia (ADH), ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and lymph node metastatic (LNMM) stages. Post-translational modifications: O-GlcNAcylation at Thr-305 and Thr-312 inhibits activating phosphorylation at Thr-308 via disrupting the interaction between AKT1 and PDPK1. O-GlcNAcylation at Ser-473 also probably interferes with phosphorylation at this site. Phosphorylation on Thr-308, Ser-473 and Tyr-474 is required for full activity. Activated TNK2 phosphorylates it on Tyr-176 resulting in its binding to the anionic plasma membrane phospholipid PA. This phosphorylated form localizes to the cell membrane, where it is targeted by PDPK1 and PDPK2 for further phosphorylations on Thr-308 and Ser-473 leading to its activation. Ser-473 phosphorylation by mTORC2 favors Thr-308 phosphorylation by PDPK1. Ser-473 phosphorylation is enhanced by interaction with AGAP2 isoform 2 (PIKE-A). Ser-473 phosphorylation is enhanced in focal cortical dysplasias with Taylor-type balloon cells. Ser-473 phosphorylation is enhanced by signaling through activated FLT3. Dephosphorylated at Thr-308 and Ser-473 by PP2A phosphatase. The phosphorylated form of PPP2R5B is required for bridging AKT1 with PP2A phosphatase. Ubiquitinated via 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination by ZNRF1, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Ubiquitinated; undergoes both 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination. TRAF6-induced 'Lys-63'-linked AKT1 ubiquitination is critical for phosphorylation and activation. When ubiquitinated, it translocates to the plasma membrane, where it becomes phosphorylated. When fully phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus, undergoes 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitination catalyzed by TTC3, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Also ubiquitinated by TRIM13 leading to its proteasomal degradation. Acetylated on Lys-14 and Lys-20 by the histone acetyltransferases EP300 and KAT2B. Acetylation results in reduced phosphorylation and inhibition of activity. Deacetylated at Lys-14 and Lys-20 by SIRT1. SIRT1-mediated deacetylation relieves the inhibition. DISEASE: Defects in AKT1 are a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]. A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. Defects in AKT1 are associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500]. Note=Genetic variations in AKT1 may play a role in susceptibility to ovarian cancer. Defects in AKT1 are a cause of Proteus syndrome (PROTEUSS) [MIM:176920]. A highly variable, severe disorder of asymmetric and disproportionate overgrowth of body parts, connective tissue nevi, epidermal nevi, dysregulated adipose tissue, and vascular malformations. Many features of Proteus syndrome overlap with other overgrowth syndromes. Similarity: Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. RAC subfamily. Contains 1 AGC-kinase C-terminal domain. Contains 1 PH domain. Contains 1 protein kinase domain. SWISS: P31749 Gene ID: 207 Database links: Entrez Gene: 207 Human Entrez Gene: 11651 Mouse Omim: 164730 Human SwissProt: O57513 Chicken SwissProt: P31749 Human SwissProt: P31750 Mouse Unigene: 525622 Human Unigene: 6645 Mouse Unigene: 11422 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |